Schizont Development: Difference between revisions
From haematologyetc.co.uk
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
Schizonts formation involves successive cycles of asexual division that eventually result in the formation of multiple separate "merozoite" forms. Those merozoites are released as the red cell breaks down then go on to infect another red cell. Schizonts therefre look very different depending on which stage of development they represent. Below are images of schizonts at different developmental stages. | |||
Revision as of 15:35, 27 March 2024
Navigation
Go Back
| How does schizont appearance change during their development?
THE INITIAL ASEXUAL DIVISION
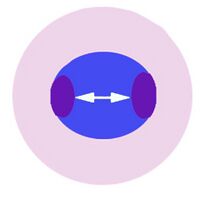
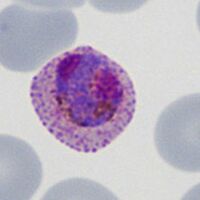
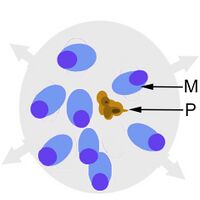
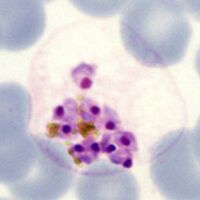
The cartoon image (A) shows the division of chromatin into two masses within a continuous blue parasite cytoplasm (indiviual merozoites are not really distinguishable here). A clinical image of a parasite at this developmental stage (P.ovale with well shown James'dots) is shown in panel (B).
IMMATURE SCHIZONT APPEARANCES
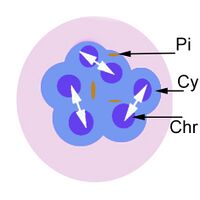
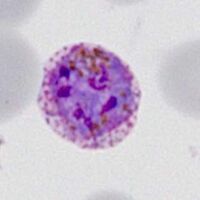
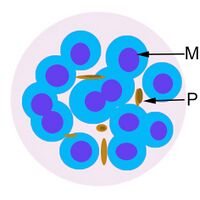
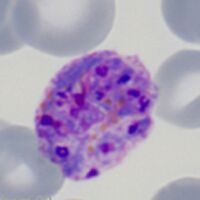
The cartoon image (A) shows the further division of chromatin (Chr) into many discrete massed within the blue parasite cytoplasm (Cy). Indiviual merozoites are still not distinguishable but the malaria pigment is obvious (Pi). A clinical image of a parasite at this developmental stage (again from P.ovale with well shown James'dots and malaria pigment) is shown in panel (B).
MATURE SCHIZONT APPEARANCES xxxxxx xxxxxx.
xxxxxx xxxxxx. |