Plasmodium ovale: Morphology: Difference between revisions
From haematologyetc.co.uk
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
<br clear=all> | <br clear=all> | ||
*Large and robust-appearing [[rings]], not usually multiply infected | |||
*Red cells may become enlarged and may be ovoid or have a [[fimbriated]] apearance | |||
*[[James' dots]] (indistinguishable from Schuffner’s dots) often appear | |||
* | *Pigment will not generally be present at the early trophozoite stage | ||
* | |||
| Line 49: | Line 47: | ||
During this growth stage parasites grows but generally retain a ring shape, this process is accompanied by further modification of the red cell with ovoid and fimbriated features more common; metabolism of haemoglobin causes malaria pigment to form. | |||
* | *Parasites become larger and thickened, but the ring form is generally retained | ||
* | *[[Red cell enlargement]] is seen and distortion causing ovoid and [[fimbriated]] forms | ||
* | *[[James’ dots]] will now be prominent in appropriately stained specimens | ||
*[[ | *[[Pigment]] will now be seen over the surface of the parasite | ||
| Line 79: | Line 77: | ||
The asexual stage of [[malaria parasite development]] - only some trophozoites form schizonts, but those that do undergo successive cycles of replication within the red cell to generate multiple [["merozoites"]] that then each invade a new red cell to continue and increase the infection. | The asexual stage of [[malaria parasite development]] - only some trophozoites form schizonts, but those that do undergo successive cycles of replication within the red cell to generate multiple [["merozoites"]] that then each invade a new red cell to continue and increase the infection. | ||
* | *A range of [[maturing schizonts]] will generally be present within moderately enlarged red cells | ||
* | *When mature schizonts may contain 16-24 separate [[merozoites]] | ||
*[[ | *[[James' dots]] can be detected in any residual cytoplasm of the erythrocyte | ||
*[[Malaria pigment|malaria pigment]] is visible in irregularly distributed clumps over the schizont surface | *[[Malaria pigment|malaria pigment]] is visible in irregularly distributed clumps over the schizont surface | ||
| Line 111: | Line 109: | ||
The sexual replication form (very distinctive). | The sexual replication form (very distinctive). | ||
* | *Red cells are very large and have ovoid or distorted forms | ||
* | *[[Macrogametocytes]] (female form) will often entirely fill the erythrocyte | ||
* | *[[Microgametocytes]] (male form) have a cytoplasmic rim with visible Schüffner's dots | ||
*[[Malaria pigment|malaria pigment]] is clumped evenly over the surface of the gametocyte | *[[Malaria pigment|malaria pigment]] is clumped evenly over the surface of the gametocyte | ||
Latest revision as of 14:26, 7 May 2024
Navigation
(click blue highlighted text to return to page)
Malaria main index
>Species identification: summary page
>>This page: P.ovale: morphology
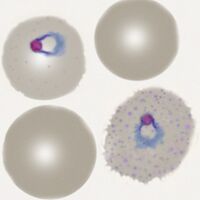
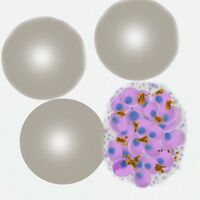
| The early trophozoite |
- Large and robust-appearing rings, not usually multiply infected
- Red cells may become enlarged and may be ovoid or have a fimbriated apearance
- James' dots (indistinguishable from Schuffner’s dots) often appear
- Pigment will not generally be present at the early trophozoite stage
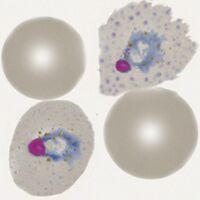
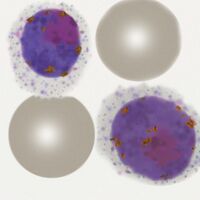
| The late trophozoite |
During this growth stage parasites grows but generally retain a ring shape, this process is accompanied by further modification of the red cell with ovoid and fimbriated features more common; metabolism of haemoglobin causes malaria pigment to form.
- Parasites become larger and thickened, but the ring form is generally retained
- Red cell enlargement is seen and distortion causing ovoid and fimbriated forms
- James’ dots will now be prominent in appropriately stained specimens
- Pigment will now be seen over the surface of the parasite
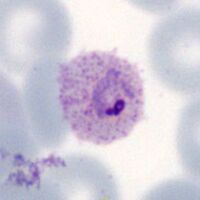
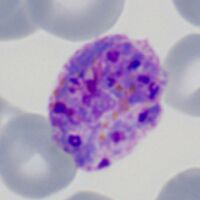
| The schizont |
The asexual stage of malaria parasite development - only some trophozoites form schizonts, but those that do undergo successive cycles of replication within the red cell to generate multiple "merozoites" that then each invade a new red cell to continue and increase the infection.
- A range of maturing schizonts will generally be present within moderately enlarged red cells
- When mature schizonts may contain 16-24 separate merozoites
- James' dots can be detected in any residual cytoplasm of the erythrocyte
- malaria pigment is visible in irregularly distributed clumps over the schizont surface
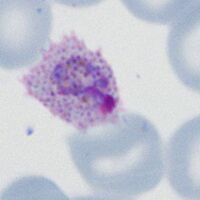
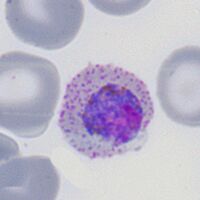
The gametocyte
| The gametocyte |
The sexual replication form (very distinctive).
- Red cells are very large and have ovoid or distorted forms
- Macrogametocytes (female form) will often entirely fill the erythrocyte
- Microgametocytes (male form) have a cytoplasmic rim with visible Schüffner's dots
- malaria pigment is clumped evenly over the surface of the gametocyte