Schüffner's dots: Difference between revisions
From haematologyetc.co.uk
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
[[Plasmodium vivax: Morphology|Go Back]] | [[Plasmodium vivax: Morphology|Go Back]] | ||
---- | ---- | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="border-style: solid; border-width: 4px; color:black" | |||
|colspan="1" style = "font-size:100%; color:black; background: FFFAFA"|<span style="color:navy>'''What are Schüffner's dots?'''</span> | |||
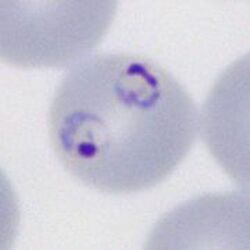
Schüffner's dots are red-purple dots seen in ''P.vivax''. They are morphologically indistinguishable from the James' dots of ''P.ovale'' but are very diffrent from the more dense and blue coloured Maurer's dots and clefts of ''P.falciparum''. Like all parasite structures Schüffner's dots form progressively, and may not be seen in very early trophozoites. | |||
<gallery mode="nolines" widths=250px heights=250px> | |||
File:11multiple1.jpg|link={{filepath:11multiple1.jpg}} | |||
</gallery> | |||
<span style="font-size:80%">The most frequent form - two early trophozoites of ''P.falciparum'' in a single erythrocyte</span> | |||
<br clear=all> | |||
---- | |||
<span style="color:navy>'''Species significance'''</span> | |||
Most often considered a feature indicating ''P.falciparum'' infection, and is certainly frequent in that species where it can be used to support the diagnosis. However, the form should not considered as specific, and may occur in any species (and is also a frequent finding for babesia parasites). | |||
---- | |||
<span style="color:navy>'''Additional images'''</span> | |||
<gallery mode="nolines" widths=200px heights=200px> | |||
File:11multiple2.jpg|A|link={{filepath:11multiple2.jpg}} | |||
File:11multiple3.jpg|B|link={{filepath:11multiple3.jpg}} | |||
File:11multiple4.jpg|C|link={{filepath:11multiple4.jpg}} | |||
</gallery> | |||
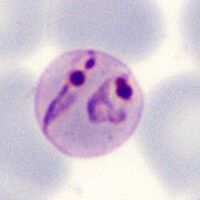
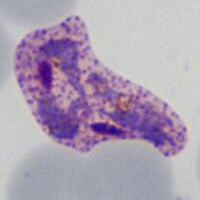
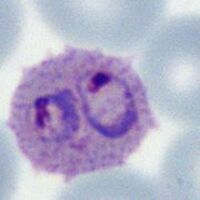
<span style="font-size:80%">Double parasites in: late trophozoite of ''P.malaria'' (A) late trophozoite of ''P.vivax'' (B) and late trophozoite of P.ovale (C)</span> | |||
| Line 16: | Line 47: | ||
| Line 22: | Line 53: | ||
These are frequent red-purple dots in the erythrocyte cytoplasm of cells infected by ''P.vivax'' (like the James' dots seen in ''P.ovale'') that develop from early trophozoite infection as faint dots, then become more obvious in all mature forms. These represent modification of the red cell by the parasite''. | These are frequent red-purple dots in the erythrocyte cytoplasm of cells infected by ''P.vivax'' (like the James' dots seen in ''P.ovale'') that develop from early trophozoite infection as faint dots, then become more obvious in all mature forms. These represent modification of the red cell by the parasite''. initially appearing as very faint dots before becoming much more intense as the parasites become more mature. Different intensities of cytoplasmic dots, from faint to intense during the development of ''P.vivax''. Note that even when faint dots are very frequent (compare with the sparse Maurer's dots and clefts of ''P.falciparum'') | ||
Revision as of 11:52, 3 April 2024
Navigation
Go Back
| What are Schüffner's dots?
Schüffner's dots are red-purple dots seen in P.vivax. They are morphologically indistinguishable from the James' dots of P.ovale but are very diffrent from the more dense and blue coloured Maurer's dots and clefts of P.falciparum. Like all parasite structures Schüffner's dots form progressively, and may not be seen in very early trophozoites.
The most frequent form - two early trophozoites of P.falciparum in a single erythrocyte
Species significance Most often considered a feature indicating P.falciparum infection, and is certainly frequent in that species where it can be used to support the diagnosis. However, the form should not considered as specific, and may occur in any species (and is also a frequent finding for babesia parasites). Additional images Double parasites in: late trophozoite of P.malaria (A) late trophozoite of P.vivax (B) and late trophozoite of P.ovale (C)
|