Boat-shaped cells: Difference between revisions
From haematologyetc.co.uk
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
<gallery mode="nolines" widths="240px" heights="240px" border="1px" > | <gallery mode="nolines" widths="240px" heights="240px" border="1px" > | ||
File: | File:Boat2A.png|link={{filepath:Boat2A.png}} | ||
File:Boat2.jpg|link={{filepath: | File:Boat2.jpg|link={{filepath:Boat2.jpg}} | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
<div style="width: 95%; overflow: auto; border: 1px solid navy; font-size:100%"> | <div style="width: 95%; overflow: auto; border: 1px solid navy; font-size:100%"> | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="color:black; background-color:#ffffff;" cellpadding="15" | {| class="wikitable" style="color:black; background-color:#ffffff;" cellpadding="15" | ||
!colspan="1" |''' | !colspan="1" |'''Inherited defects of haemoglobin with sickling tendency''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |Sickle cell disease (HbSS) | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Compound heterozygote of sickle haemoglobin and haemoglobin C (HbSC) | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | |Compound heterozygote with betathalassaemia (HbSbeta thalassaemia) | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Clinical Examples | ---- | ||
'''Clinical Examples''' | |||
<gallery widths="250px" heights="250px" > | <gallery widths="250px" heights="250px" > | ||
File: | File:Boat3.jpg|link={{filepath:Boat3.jpg}} | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
<span style="font-style:italic; font-size:90%;'' > | <span style="font-style:italic; font-size:90%;'' > | ||
Clinical Image 1 There are many elongated cells in this image, ranging from a very typical sickle cell through to a fairly typical boatshaped cell. Cells with form intermediate to the entirely typical sickle and boat cells are frequent. Clinical condition: sickle cell disease. | Clinical Image 1 There are many elongated cells in this image, ranging from a very typical sickle cell through to a fairly typical boatshaped cell. Cells with form intermediate to the entirely typical sickle and boat cells are frequent. Clinical condition: sickle cell disease. | ||
</span> | </span> | ||
<gallery widths="250px" heights="250px" > | |||
File:Boat4.jpg|link={{filepath:Boat4.jpg}} | |||
</gallery> | |||
<span style="font-style:italic; font-size:90%;'' > | |||
Clinical Image 2 While the target cells and contracted cells are the most immediately obvious red cell forms on this image, there are also a number of entirely typical boat shaped forms present. Clinical condition: Haemoglobin SC disease | Clinical Image 2 While the target cells and contracted cells are the most immediately obvious red cell forms on this image, there are also a number of entirely typical boat shaped forms present. Clinical condition: Haemoglobin SC disease | ||
</span> | |||
<gallery widths="250px" heights="250px" > | |||
File:Boat5.jpg|link={{filepath:Boat5.jpg}} | |||
</gallery> | |||
<span style="font-style:italic; font-size:90%;'' > | |||
Clinical Image 3 this case there is a boat shaped cell in the upper centre of the image this perhaps illustrates well the alternative name “kissing lip cells Note also the microcytosis (use the nuclear size of the small lymphocyte cell for reference). Clinical condition: Haemoglobin S beta thalassaemia '' | Clinical Image 3 this case there is a boat shaped cell in the upper centre of the image this perhaps illustrates well the alternative name “kissing lip cells Note also the microcytosis (use the nuclear size of the small lymphocyte cell for reference). Clinical condition: Haemoglobin S beta thalassaemia '' | ||
</span> | |||
Pathobiology | ---- | ||
'''Pathobiology''' | |||
Like sickle cells, this cell form arises as a result of altered haemoglobin solubility and the formation of long polymers along the cell length when deoxygenated. | Like sickle cells, this cell form arises as a result of altered haemoglobin solubility and the formation of long polymers along the cell length when deoxygenated. | ||
---- | |||
Latest revision as of 23:00, 26 March 2023
Derivation: descriptive term derived from resemblance to a canoe viewed from above (or a pair of lips)
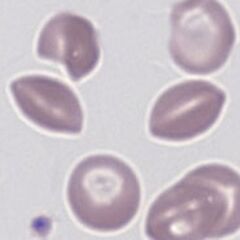
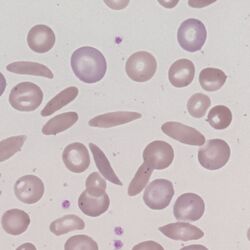
Appearance
An elliptical cell with sharpened ends and an elongated and sharpened area of central pallor; the cells are broader than a typical sickle cell and lack the characteristic curve.
Images Boat shaped cells. The cell body may be dense or normal, but retains central pallor. The appearance is that of a canoe viewed from above with sharpened ends an appearance reflected in the area of central pallor which also has a sharp appearance, although this may also be more slit-like in some cells. Where present the cells are generally frequent and will be accompanied by other features of the underlying abnormal haemoglobin. This may include typical sickle cells, contracted red cells, target cells or other features depending on clinical context.
Significance
These cells are formed in the presence of abnormal haemoglobin. Although most closely associated with classical sickle disease (HbSS), boatshaped cells are also seen in compound heterozygotes between HbS and other abnormal haemoglobins (see causes).
Pitfalls
Providing the typical sharp ends are present in both cell and area of pallor this form is fairly distinctive and generally numerous.
| Inherited defects of haemoglobin with sickling tendency |
|---|
| Sickle cell disease (HbSS) |
| Compound heterozygote of sickle haemoglobin and haemoglobin C (HbSC) |
| Compound heterozygote with betathalassaemia (HbSbeta thalassaemia) |
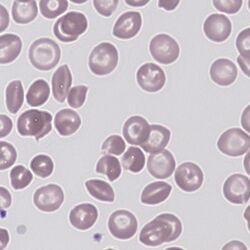
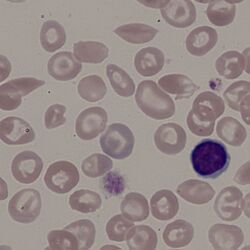
Clinical Examples
Clinical Image 1 There are many elongated cells in this image, ranging from a very typical sickle cell through to a fairly typical boatshaped cell. Cells with form intermediate to the entirely typical sickle and boat cells are frequent. Clinical condition: sickle cell disease.
Clinical Image 2 While the target cells and contracted cells are the most immediately obvious red cell forms on this image, there are also a number of entirely typical boat shaped forms present. Clinical condition: Haemoglobin SC disease
Clinical Image 3 this case there is a boat shaped cell in the upper centre of the image this perhaps illustrates well the alternative name “kissing lip cells Note also the microcytosis (use the nuclear size of the small lymphocyte cell for reference). Clinical condition: Haemoglobin S beta thalassaemia
Pathobiology
Like sickle cells, this cell form arises as a result of altered haemoglobin solubility and the formation of long polymers along the cell length when deoxygenated.